About Us

About Company
Professional and Expert Roofing Contractor

Max Stewart
FOUNDER
Need help? Contact me
+1 2345 678 or info@example.com
Our History
Superior Roofing Services


1993 - 2017
Our Most Efficient Year
Vestibulum ac diam sit amet quam vehicula elementum sed sit amet dui. Curabitur aliquet quam id dui posuere blandit. Vestibulum ac diam sit amet quam vehicula elementum sed sit amet dui. Sed porttitor lectus nibh.
Working With The Best
Our Partners




Mission solar panels generally receive positive reviews for their durability and reliability, often being praised for being built to withstand extreme weather and exceeding industry standards. They are a U.S.-based company, and while some reviews note their efficiency might not be the absolute highest on the market, they are frequently considered a strong value with good long-term performance.
- Durability: The panels are known for being exceptionally tough, built to withstand extreme weather, high winds, and even hail.
- Reliability: They undergo rigorous testing to ensure long-term performance and reliability.
- U.S.-based: They are manufactured and headquartered in San Antonio, Texas, which can be a benefit for customers who prefer American-made products.
- Good value: While efficiency may not be top-tier, they are considered a strong choice for homeowners seeking a durable and reliable panel at a competitive price.
- Efficiency: Some of Mission Solar’s panels may have lower efficiency ratings compared to other brands that have higher-end models.
- Newer to market: While growing in popularity, they have a shorter history than some of the oldest solar panel manufacturers

This Vedio Provides a full review of mission Solar Panels disscussing thier performance and efficiency
Our Company Profile

ABOUT US
JANGID Solar Energy Pvt. Ltd. is a globally recognized
leading solar energy solutions provider, specializing in
high efciency PV module comprehensive EPC solutions.
We are working in Institutions, Residential Colonies, Ofce
Buildings using Electricity on Large Scale, Schools, Colleges,
Universities, Government Ofces, Giant Industries, Film
Makers, Hotels, Restaurants, Cinema Halls, Terrace House
Etc.
What WE DO

- Our USP is our ability to create customized solutions to meet
and exceed the needs of the customer – both in terms of
budget and future requirements. Our recommendations are
robust since they are based on years of experience and an
in-depth understanding of this market and the best products
available. Our experts will guide you through every step
such that you make a decision to buy, only if the system will
serve your needs and would be within your budget.
Our team is abreast with the latest REC values, FITs, other
government rebates and schemes in addition to
environmental needs. They are passionate about renewable
energy solutions and each one is highly skilled in their
respective area of work.
Our company has installed several systems of all kinds and
sizes throughout the cross-section of the country and have
helped homeowners, industries, other commercial
establishments and schools. We are proud to say that we
have a happy customer base and would be glad to help you
save money by generating your own energy to meet your
needs, while ensuring that the environment is safe too.
Start Solar consistently endeavours to be a strategic and
collaborative partner with each client and strives to improve
the community and the environment.
- US Solar: A developer, owner, and operator of solar projects, with a special focus on making solar energy accessible through community solar programs.
- First Solar: Known as “America’s Solar Company,” it focuses on building innovative solar solutions to meet the country’s energy needs.
- Sunrun: A leading residential solar company in the US, serving over a million customers and installing a significant amount of solar capacity.
- U-Solar Clean Energy: Provides solar power solutions for industrial, commercial, and residential sectors.
- Usha Shriram Solar: Aims to provide clean and sustainable energy through solar power solutions, focusing on quality of life and environmental benefits.
- SunSource Energy: A leading C&I focused solar power company that offers flexible solar solutions through the “Open Access” route.
- Solar Energy Corporation of India (SECI): An implementing agency for solar and other renewable energy projects, and also a power trading company.
- Emmvee: Started in 1992, it is a leading manufacturer of solar water heating systems and also provides solar panels.
- Tata Power Solar: A prominent company in India that manufactures solar panels for home and industrial needs and plays a role in the country’s sustainable power production goals.
- What solar companies do
- Project development and ownership: Develop, own, and operate large-scale solar farms and smaller community projects.
- Solutions for clients: Provide solar power solutions for residential, commercial, and industrial clients, including installation and maintenance services.
- Consultancy services: Offer services like feasibility studies and project management consultancy to government and other entities.
- Power trading: Procure and trade solar and renewable energy power on a pan-India basis.
Which Solar Panel is No 1 . in India
Tata is the Most Trusted and Largest solar manufacturer in India for Home, Residential, and Industrial requirements.. Tata solar plays an important role in making India as a leading sustainable solar power producer country.


Features Of Tata Solar Panel
- Solar: Offers solar panels for both residential rooftops and large-scale projects, with features like high-efficiency, low-light performance, and durability.
- Wind: Provides wind energy solutions, contributing to clean energy transformation.
- Hydro: Generates electricity through hydropower.
- Largest charging network: Has an extensive network of home, public, and captive EV chargers across India.
- EZ Charge platform: Provides end-to-end solutions from home chargers to fast-charging stations, supported by a mobile app to locate points and make payments.
- Supports sustainable mobility: Facilitates the shift to electric mobility with its charging infrastructure and RTS solutions.
- EZ HOME: An IoT-based system for home automation that allows users to control appliances like lights, fans, and ACs through a smartphone app or voice commands.
- Voice control: Integrates with Google Assistant and Alexa for hands-free control.
- Energy management: Includes features like real-time energy monitoring, scheduling, and “scene creation” for controlling multiple devices at once.
- Safety: Offers overload protection for devices.
- Remote operation: Allows for remote monitoring and control of home appliances.
- Transmission and Distribution: Builds and maintains the infrastructure that links power to progress.
- Advanced Distribution Management System (ADMS): An integrated platform for real-time control and supervision of the power network.
- Automated Power Restoration System (APRS): An advanced system within ADMS that automatically isolates faults and restores power to consumers with minimal delay.
- Customer portal: Provides online access to manage accounts, check meter readings, view bills, and track consumption history.
- Power trading: Offers solutions for power trading and portfolio management for renewable energy investments
Tata Power is a leading integrated power company in India and part of the Tata group, with operations across the entire power value chain, including generation, transmission, distribution, and trading. It has a diversified portfolio of both renewable (solar, wind) and conventional (thermal, hydro) energy sources, with a significant focus on shifting towards sustainable and clean energy solutions like EV charging, smart meters, and rooftop solar. The company was founded in 1915 and has a long history of pioneering power projects in India.
- Integrated operations:
The company generates, transmits, and distributes electricity, serving a broad range of residential and commercial customers.
- Generation sources:
Its energy generation comes from a mix of sources, including coal, gas, hydro, solar, and wind power.
- Focus on renewables:
Tata Power is strategically shifting towards clean energy, with 40% of its total capacity coming from renewables and a commitment to becoming carbon neutral by 2045.
- Innovative energy solutions:
It is expanding into new areas such as electric vehicle (EV) charging, solar pumps, microgrids, and energy storage to become a comprehensive energy solutions provider.
- History and legacy:
Established in 1915, it commissioned India’s first clean energy station and has a history of significant milestones in the country’s power sector development.
- Geographic reach:
While its distribution network reaches millions of customers in various Indian cities, its operations extend to multiple geographic locations across India.
- Headquarters:The company is headquartered in Mumbai, Maharashtra


- Registered Office: Corporate Center B, 34 Sant Tukaram Road, Carnac Bunder, Mumbai – 400 009, Maharashtra.
- Tata Power Trading Company Ltd (Head Office): B-12 & 13, 2nd Floor, Shatabadi Bhawan, Sector 4, Noida, Delhi

What is The Cost of Tata Solar Panel
A 5kW Tata solar system costs approximately Rs. 2,50,000 to Rs. 3,50,000 in India, depending on the components included. This system is ideal for larger households or small businesses requiring substantial energy output.
There is no single “No. 1” solar panel, as rankings can differ based on criteria like manufacturing capacity, efficiency, or specific market segments. However, Waaree Energies, Tata Power Solar, and Adani Solar are consistently ranked among the top manufacturers in India by various sources, notes Waaree Energies, Novasys Green, and Evolve Energy Group. Other prominent companies include Vikram Solar, Goldi Solar, and Loom Solar.
- Waaree Energies:Frequently listed among the largest and most trusted solar panel manufacturers in India, known for its extensive manufacturing and export reach.
- Tata Power Solar:A leading name in the industry, recognized for its high-quality products and solutions for various solar projects.
- Adani Solar:A key player in the Indian solar market, offering both panels and comprehensive solutions for different types of projects.
- A major manufacturer known for high-efficiency panels and a strong reputation.
- Another prominent manufacturer with significant production capacity.
- Has gained a strong reputation for high-quality and innovative products, particularly for residential applications.
- An integrated manufacturer of solar modules and key components, with a strong presence both domestically and internationally.
Prices Range Of Solar Panel.
The price of a 3kW Tata solar system typically ranges between Rs. 1,50,000 and Rs. 2,00,000 in India. This includes high-quality solar panels, an inverter, and installation services, offering reliable performance and long-term durability.



Solar Panel How it Work in Winter
Solar panels still work during snowfall by using sunlight that penetrates light snow, while dark, tilted panels naturally melt or shed heavy snow, often aided by the sun. Although efficiency decreases with heavy coverage, cold, clear post-snow conditions can boost performance via the "albedo effect" (reflected sunlight), and snow cleaning the panels as it melts.
This video demonstrates how solar panels continue to generate electricity even when covered with snow:
- Generation with Snow: Panels still generate electricity through light, powdery snow or partial coverage.
- Melting & Sliding: Dark-colored panels absorb heat from the sun and, being mounted at an angle (typically 30−45∘30 minus 45 raised to the composed with power
30−45∘
), allow snow to slide off efficiently.
- Optimal Angle: A steeper tilt, closer to 45∘45 raised to the composed with power
45∘
, is generally better for shedding snow in colder climates.
- The Albedo Effect: Sunlight reflecting off snow-covered ground onto the panels can increase energy production, provided the panels themselves are clear.
- Performance: While heavy, wet snow can cause 0-30% efficiency (or total blockage), light snow typically results in 80-90% performance.
- Safety: The weight of heavy snow can stress mounting structures. Manual removal is generally unnecessary, but if done, it should be done carefully with a soft brush to avoid damage.
- Performance with Snow: While snow blocks sunlight, light snow often slides off easily due to the panel’s tilt (typically 30-45 degrees). A small amount of snow rarely stops energy production entirely.
- The Albedo Effect: Snow on the ground acts as a mirror, reflecting extra sunlight onto the panels, which can increase energy production by 5–15%.
- Temperature Advantages: Photovoltaic cells actually work more efficiently in cold, clear weather.
- Snow Clearing: Generally, manual clearing is not necessary, as the sun and gravity will clear the panels. If needed, a soft brush on a long handle can be used, but safety should be the priority.
- Weight Load: While snow can be heavy, modern panels are designed to handle, and are tested for, significant snow loads.
This video explains how solar panels can still produce power in the snow.
This video provides a visual explanation of how solar panels convert sunlight int
- Absorption: PV cells, composed of silicon, absorb photons (light particles) from the sun.
- Absorption: PV cells, composed of silicon, absorb photons (light particles) from the sun
- Electron Excitation: The energy from photons knocks electrons loose from atoms, creating an electric charge.
- Current Generation: An internal electric field forces these loose electrons to flow, creating a, electrical current.
- Conversion: The generated DC electricity flows to an inverter, which converts it into AC electricity, allowing it to power appliances.
- Distribution: The AC electricity is sent to the home’s electric panel, or stored in batteries.
- PV Cells: The fundamental unit, usually arranged into panels and arrays.
- Inverter: Crucial component for converting DC to AC.
- Types: Monocrystalline panels (most efficient), polycrystalline panels, and thin-film.
- Solar Thermal: A different type of panel that heats water instead of generating electricity.
o electricity:
How does solar power work?
Solar power works by converting energy from the sun into power. There are two forms of energy generated from the sun for our use – electricity and heat.
Both are generated through the use of solar panels, which range in size from residential rooftops to ‘solar farms’ stretching over acres of rural land.
Is solar power a clean energy source?
Yes, solar power is a renewable and infinite energy source that creates no harmful greenhouse gas emissions – as long as the sun continues to shine, energy will be released.
The carbon footprint of solar panels is already quite small, as they last for over 25 years. Plus, the materials used in the panels are increasingly recycled, so the carbon footprint will continue to shrink.
When was solar power discovered?
Solar energy was used by humans as early as the 7th century B.C. when humans used sunlight to light fires by reflecting the sun’s rays onto shiny objects. Later, in 3rd century B.C., the Greeks and Romans harnessed solar power with mirrors to light torches for religious ceremonies.
In 1839 and at the age of just 19, French physicist Edmond Becquerel discovered the photovoltaic (PV) effect while experimenting with a cell made of metal electrodes in a conducting solution. He noted that the cell produced more electricity when it was exposed to light – it was a photovoltaic cell.
In 1954 PV technology was born when Daryl Chapin, Calvin Fuller and Gerald Pearson developed the silicon PV cell at Bell Labs in 1954 – the first solar cell capable of absorbing and converting enough of the sun’s energy into power to run everyday electrical equipment.
Today satellites, spacecraft orbiting Earth, are powered by solar energy.
How exactly is electricity from solar energy produced?
Solar panels are usually made from silicon, or another semiconductor material installed in a metal panel frame with a glass casing. When this material is exposed to photons of sunlight (very small packets of energy) it releases electrons and produces an electric charge.
This PV charge creates an electric current (specifically, direct current or DC), which is captured by the wiring in solar panels. This DC electricity is then converted to alternating current (AC) by an inverter. AC is the type of electrical current used when you plug appliances into normal wall sockets.

What’s the difference between solar PV panels and solar thermal panels?
Solar PV panels generate electricity, as described above, while solar thermal panels generate heat. While the energy source is the same – the sun – the technology in each system is different.
Solar PV is based on the photovoltaic effect, by which a photon (the basic unit of light) impacts a semi-conductor surface like silicon and generates the release of an electron. Solar thermal is less sophisticated and simply the direct heating of water (or other fluids) by sunlight. For domestic use, solar thermal panels are also installed on a roof facing the sun, heating water stored in a hot water cylinder and so providing hot water and heating. On a larger scale, solar thermal can also be used in power stations.
What are solar farms?
Solar farms, also known as solar parks or solar fields, are large areas of land containing interconnected solar panels positioned together over many acres, to harvest large amounts of solar energy at the same time. Solar farms are designed for large-scale solar energy generation that feed directly into the grid, as opposed to individual solar panels that usually power a single home or building.
Can solar power be generated on a cloudy day?
Yes, it can – solar power only requires some level of daylight in order to harness the sun’s energy. That said, the rate at which solar panels generate electricity does vary depending on the amount of direct sunlight and the quality, size, number and location of panels in use.
Who are the largest producers of solar power worldwide?
As of 2022, China is the largest producer of solar powered electricity generation in the world. The US comes in second, followed by Japan, Germany and India.1
How is more solar power being brought into our electricity systems?
Both the UK and US governments are aiming to decarbonise their electricity systems by 2035, in which renewable energy sources like solar power are set to play a major part.
Solar energy in the UK
The UK’s first transmission-connected solar farm was energised in May 2023. This was the first PV solar array to feed electricity directly into the UK’s transmission network, allowing it to be transported over greater distances. Previously, UK solar farms were connected to the country’s distribution networks – the lower-voltage regional grids that carry power from the high-voltage transmission network to homes and businesses.
Located near Bristol, this solar plant is expected to generate over 73,000 megawatt hours (MWh) annually – enough to power the equivalent of over 17,300 homes – and will displace 20,500 tons of CO2 each year compared to traditional energy production.
The UK government’s Powering up Britain report has reaffirmed its ambition for a five-fold increase in deployment of solar generation by 2035, with up to 70 gigawatt (GW) installed – enough to power around 20 million homes.
Read more about the UK’s first transmission-connected solar farm
Solar energy in the US
The Solar Futures Study, released by the U.S. Department of Energy (DoE) in 2021, discusses their blueprint for a zero-carbon grid and the significant role solar will play in decarbonising the country’s power grid. According to the study, 40% of the nation’s electricity has the potential to be powered by solar energy by 2035.
In April 2023, the Biden-Harris administration announced an $82 million investment to fund technologies that will help integrate solar energy into the grid. The investment will increase domestic solar manufacturing and recycling, which will help to strengthen the clean energy grid in the US.
Last updated: 16 May 2023
The information in this article is intended as a factual explainer and does not necessarily reflect National Grid’s strategic direction or current business activities.
More energy explained
What is net zero?
The amount of sunlight that strikes the earth’s surface in an hour and a half is enough to handle the entire world’s energy consumption for a full year. Solar technologies convert sunlight into electrical energy either through photovoltaic (PV) panels or through mirrors that concentrate solar radiation. This energy can be used to generate electricity or be stored in batteries or thermal storage.
Below, you can find resources and information on the basics of solar radiation, photovoltaic and concentrating solar-thermal power technologies, electrical grid systems integration, and the non-hardware aspects (soft costs) of solar energy. You can also learn more about how to go solar and the solar energy industry. In addition, you can dive deeper into solar energy and learn about how the U.S. Department of Energy Solar Energy Technologies Office is driving innovative research and development in these areas.
Solar Energy 101
Solar radiation is light – also known as electromagnetic radiation – that is emitted by the sun. While every location on Earth receives some sunlight over a year, the amount of solar radiation that reaches any one spot on the Earth’s surface varies. Solar technologies capture this radiation and turn it into useful forms of energy. Learn about the basics of solar radiation.
There are two main types of solar energy technologies—photovoltaics (PV) and concentrating solar-thermal power (CSP).
Photovoltaics Basics
You’re likely most familiar with PV, which is utilized in solar panels. When the sun shines onto a solar panel, energy from the sunlight is absorbed by the PV cells in the panel. This energy creates electrical charges that move in response to an internal electrical field in the cell, causing electricity to flow.
 Learn the basics of how photovoltaic (PV) technology works with these resources from the DOE Solar Energy Technologies Office.
Learn the basics of how photovoltaic (PV) technology works with these resources from the DOE Solar Energy Technologies Office. Solar photovoltaic modules are where the electricity gets generated, but are only one of the many parts in a complete photovoltaic (PV) system.
Solar photovoltaic modules are where the electricity gets generated, but are only one of the many parts in a complete photovoltaic (PV) system.
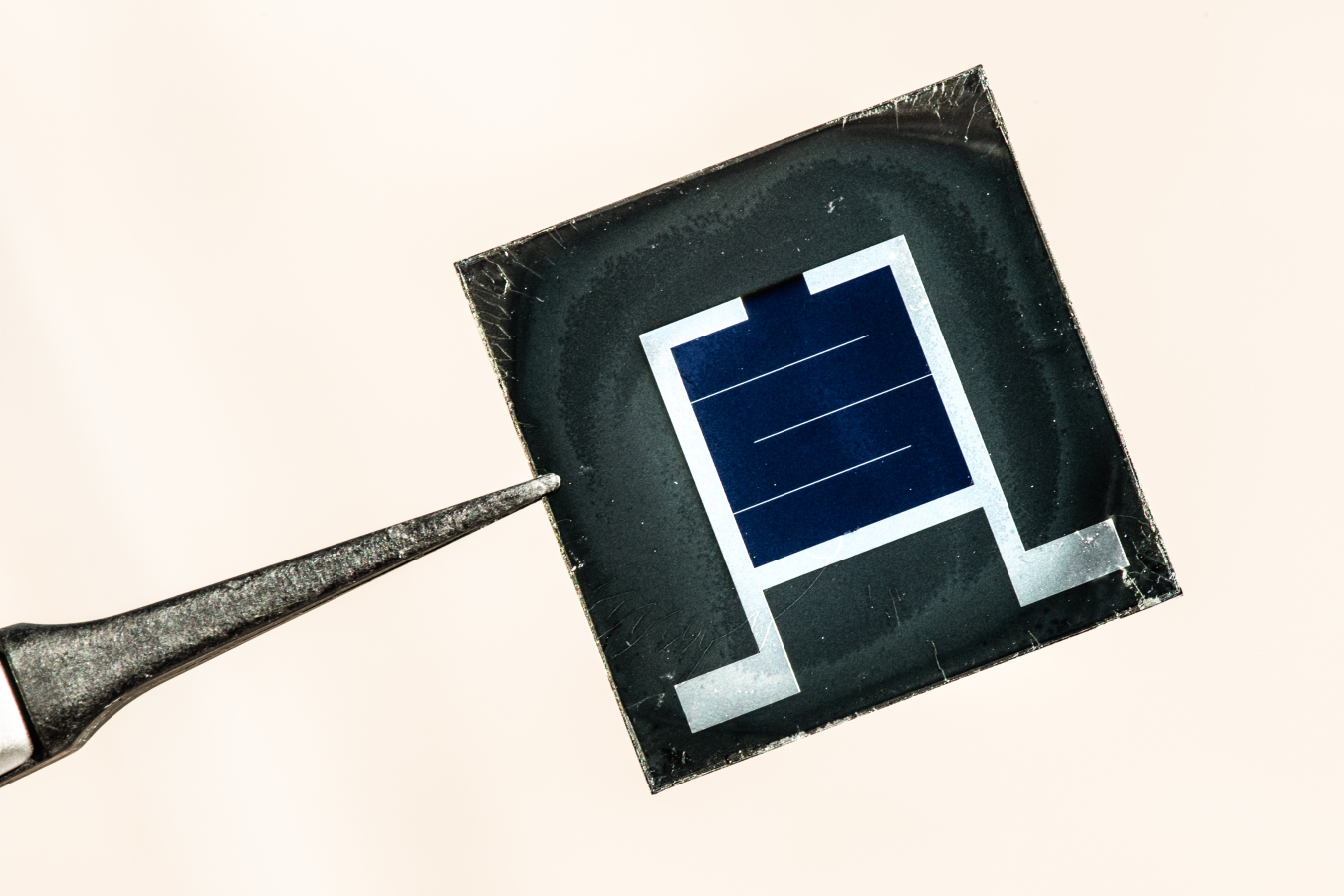 Part 1 of the PV Cells 101 primer explains how a solar cell turns sunlight into electricity and why silicon is the semiconductor that usually does it.
Part 1 of the PV Cells 101 primer explains how a solar cell turns sunlight into electricity and why silicon is the semiconductor that usually does it. Improving photovoltaic (PV) efficiency is a key goal of research and helps make PV technologies cost-competitive with conventional sources of energy.
Improving photovoltaic (PV) efficiency is a key goal of research and helps make PV technologies cost-competitive with conventional sources of energy.
Concentrating Solar-Thermal Power Basics
Concentrating solar-thermal power (CSP) systems use mirrors to reflect and concentrate sunlight onto receivers that collect solar energy and convert it to heat, which can then be used to produce electricity or stored for later use. It is used primarily in very large power plants.
 Learn the basics of how concentrating solar-thermal power (CSP) works with these resources from the DOE Solar Energy Technologies Office.
Learn the basics of how concentrating solar-thermal power (CSP) works with these resources from the DOE Solar Energy Technologies Office. One challenge facing solar energy is reduced energy production when the sun sets or is blocked by clouds. Thermal energy storage is one solution.
One challenge facing solar energy is reduced energy production when the sun sets or is blocked by clouds. Thermal energy storage is one solution.
 In power tower concentrating solar power systems, several flat, sun-tracking mirrors focus sunlight onto a receiver at the top of a tall tower
In power tower concentrating solar power systems, several flat, sun-tracking mirrors focus sunlight onto a receiver at the top of a tall tower- Linear concentrating solar power (CSP) collectors capture the sun’s energy with large mirrors that reflect and focus the sunlight on a linear receiver
Systems Integration Basics
Solar energy technology doesn’t end with electricity generation by PV or CSP systems. These solar energy systems must be integrated into homes, businesses, and existing electrical grids with varying mixtures of traditional and other renewable energy sources.
 Learn the basics of how solar energy technologies integrate with electrical grid systems through these resources from the DOE Solar Energy Office.
Learn the basics of how solar energy technologies integrate with electrical grid systems through these resources from the DOE Solar Energy Office. This page explains what an inverter is and why it’s important for solar energy generation.
This page explains what an inverter is and why it’s important for solar energy generation.
 This resource page looks at ways to ensure continuous electricity regardless of an unforeseen event are by using distributed energy resources.
This resource page looks at ways to ensure continuous electricity regardless of an unforeseen event are by using distributed energy resources. Storage helps solar contribute to the electricity supply even when the sun isn’t shining by releasing the energy when it’s needed.
Storage helps solar contribute to the electricity supply even when the sun isn’t shining by releasing the energy when it’s needed.
Soft Costs Basics
A number of non-hardware costs, known as soft costs, also impact the cost of solar energy. These costs include permitting, financing, and installing solar, as well as the expenses solar companies incur to acquire new customers, pay suppliers, and cover their bottom line. For rooftop solar energy systems, soft costs represent the largest share of total costs.
 Learn the basics of what solar soft costs are and how they impact solar energy adoption with resources from the DOE Solar Energy Technologies Office.
Learn the basics of what solar soft costs are and how they impact solar energy adoption with resources from the DOE Solar Energy Technologies Office. As the solar energy market expands, alternative business models like community solar are gaining popularity.
As the solar energy market expands, alternative business models like community solar are gaining popularity.
- Solar workforce development includes online training, on-the-job training, curriculum development, and other activities that prepare people for solar.
Going Solar Basics
Solar energy can help to reduce the cost of electricity, contribute to a resilient electrical grid, create jobs and spur economic growth, generate back-up power for nighttime and outages when paired with storage, and operate at similar efficiency on both small and large scales.
 When it comes to installing solar, our resources can help you determine the best options.
When it comes to installing solar, our resources can help you determine the best options. If you are an agricultural land owner and are considering your options to go solar, here are some resources to help you decide what’s best for you.
If you are an agricultural land owner and are considering your options to go solar, here are some resources to help you decide what’s best for you.
 To help consumers quantify the potential benefits of going solar, national laboratories and private companies have developed a number of tools.
To help consumers quantify the potential benefits of going solar, national laboratories and private companies have developed a number of tools. As the solar energy market expands, alternative business models like community solar are gaining popularity.
As the solar energy market expands, alternative business models like community solar are gaining popularity.
Solar Industry Basics
Solar energy systems come in all shapes and sizes. Residential systems are found on rooftops across the United States, and businesses are also opting to install solar panels. Utilities, too, are building large solar power plants to provide energy to all customers connected to the grid.
 Each quarter, NREL conducts a presentation of technical trends within the solar industry.
Each quarter, NREL conducts a presentation of technical trends within the solar industry. These resources help those looking to find employment in the hundreds of thousands of jobs in the U.S. solar industry.
These resources help those looking to find employment in the hundreds of thousands of jobs in the U.S. solar industry.
Dive Deeper
Learn more about the innovative research the Solar Energy Technologies Office is doing in these areas.
In addition to this basic information about solar energy, you can find more solar energy information resources here.




